Flat file user databases are used to list all the legitimate
users for the <AuthBy FILE> module. You can also use flat file user
databases as input to the builddbm and
buildsql utility to create a DBM user database. See
the users file in the Radiator distribution for an
example.
Flat file user databases are ASCII text files containing
zero or more user definitions. Lines beginning with ‘#’ are ignored. Each
user definition is one or more lines. The first line must start with the
user name in the first column. Subsequent lines for the user must begin
with white space.
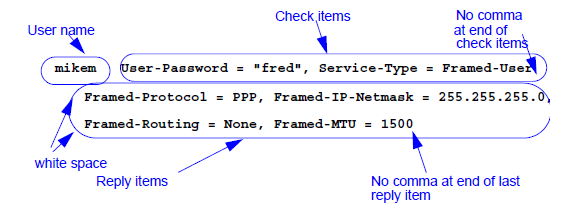
User names are quoted with double quotes (") if
they contain white space. The user name must be followed by white space,
followed by zero or more check items. Each check item is in the form
Attribute = Value, and it defines a RADIUS attribute
that is checked in Access-Requests before the user is authenticated.
Multiple check items are separated by commas. There must be no comma after
the last check item in the line. Values may optionally be surrounded by
double quotes, which are ignored. For more information about check items,
see
Section 7. Check and reply items.
The second and
subsequent lines are ‘reply’ items. Each line must commence with white
space. Each reply item is in the form “Attribute = Value”, and it defines
a RADIUS attribute that are returned to the NAS if the authentication
succeeds. Such reply items are generally used to configure the NAS for the
user. Each reply item must have a trailing comma (‘,’) except the last
item on the last line. Values may optionally be surrounded by double
quotes, which are ignored. Reply item values support special formatting
characters, see
Section 3.3. Special formatters.
The following
figure shows an example, if the user mikem is granted
access, the modem is configured for Framed-Protocol of PPP, and IP netmask
of 255.255.255.0, Framed-Routing of None and a Framed-MTU of 1500.
Figure 5. Typical user entry in a flat file user database