-hThis prints the usage log and
exits.
-timeThis is an alias for
-print_stats.
-iterations nThis sends all the selected
requests n times, instead of just once.
-iteration_delay fThis option makes
radpwtst to wait for specified amount of time
between iterations. For example, when setting
iteration_delay to 0.01,
radpwtst waits 0.01 seconds between iterations.
This option is useful in testing purposes or when packet rate needs to
be limited. Note that delay can be specified as float.
-timestampsThis includes a time stamp in
announce messages. This option is automatically enabled when
iterations is set to a value larger than
1.
-log_microsecondsUsing this, the timestamps
are logged in microseconds instead of seconds.
-trace [n]This prints useful trace
information, including the full contents of all transmitted and received
requests. The default is to print limited information from the reply.
Trace level 5 produces hex packet dumps of requests and replies. The
trace level is optional and the default value is
1.
-notraceThe trace information is not
printed. The default is to print limited information from the
reply.
-onlyfailedThis shows only the failed
requests.
-print_statsUsing this,
radpwtst prints the the statistics of all requests
and elapsed time taken to send and receives all iterations when it is
finished and calculates packet rate for packets sent.
This is useful
for testing purposes, since it measures how fast the RADIUS server
handles requests. If Perl Time::HiRes module is
available, the elapsed time is printed with sub-second resolution. This
module is available in all recent Perl distributions.
To get useful
values, the number of iterations must be large enough, for example,
8000.
-user usernameThis tags the requests with
User-Name of username. The default value is
mikem.
-password passwordIn Access-Requests, the
password is password. The default value is
fred.
-s serverThis sends all the requests to the
server, which can be either the IP address or the DNS name of the host
where the destination RADIUS server runs. The default value is
localhost.
-secret secretThis uses secret as the shared
secret. The default value is mysecret.
-auth_port portThis is the port to use for
authentication requests . The default value is
1645.
-acct_port portThis is the port to use for
accounting requests. The default value is
1646.
-noauthAccess-Request is not sent.
-noacctAccounting-Request is not
sent.
-nostartAccounting-Request Start is not
sent.
-nostopAccounting-Request Stop is not
sent.
-aliveThis sends an Accounting-Request with
Acct-Status-Type of Alive.
-statusThis sends a Server-Status. The
contents of the reply are printed.
Note
The Status-Server RFC
requires Message-Authenticator. In most cases you need the
-message_authenticator option also.
-chapAuthentication is done with CHAP,
instead of PAP.
-chap_ncAuthenticate with CHAP, instead of
PAP, with the CHAP Challenge in the authenticator, and not in a separate
CHAP-Challenge attribute.
-mschapAuthentication is done with MSCHAP,
instead of PAP or CHAP. Requires Digest-MD4-1.0 or better from CPAN. For
more information about CPAN, see
Section 2.1.2. CPAN.
-mschapv2Authentication is done with MSCHAP
V2, instead of MSCHAP, PAP or CHAP. This requires Digest-MD4 version 1.1
or better and Digest-SHA version 5.0 or better from CPAN. For more
information about CPAN, see
Section 2.1.2. CPAN.
-sipSIP Digest is done authentication as per
draft-sterman-aaa-sip-00.txt. This requires special
attributes in the additional dictionary.sip in your
distribution, so it should be used with -dictionary
dictionary,dictionary.sip.
-eapmd5Authentication is done with EAP-MD5.
This usually involves 2 requests being sent to the server. The first is
the EAP Identity, the second is the EAP-MD5 response.
-eapotpAuthentication is done with EAP-One
Time Password. This usually involves 2 requests being sent to the
server. The first is the EAP Identity, the second is the EAP-One Time
Password response.
-eapgtcAuthentication is done with
EAP-Generic Token Card. This usually involves 2 requests being sent to
the server. The first is the EAP Identity, the second is the EAP-Generic
Token Card response.
-eapfastgtcThis is similar as
-eapgtc argument: authentication is done with
EAP-Generic Token Card. This usually involves 2 requests being sent to
the server. The first is the EAP Identity, the second is the EAP-Generic
Token Card response. However, this uses RFC 5421 EAP-FAST-GTC response
format.
-leapEAP-LEAP authentication is done. This
usually involves 3 requests being sent to the server. The first is the
EAP Identity, the second is the LEAP client response and the third is
the LEAP Access Point Challenge.
-motp_secret xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxThis makes
Mobile OTP request using the password as PIN and motp_secret as the MOTP
secret key.
-eaphex xxxxxxxxxxxThis adds an EAP-Message
attribute to the request. Argument is the message contents in hex. The
correct Message-Authenticator is automatically added.
-interactiveThis displays the Reply-Message,
reads a new password from STDIN, and sends a new Access-Request,
automatically copying any State attribute to the new request. This flag
is useful for testing methods like <AuthBy ACE> which use
Access-Challenge to prompt the user during a series of steps in an
authentication conversation.
This flag is also useful if password
needs to be kept secret. When -interactive is set, password is read
without local echo.
Requires Perl module Term::Readkey on Windows.
Some Unix-based systems are supported directly but Term::ReadKey is
recommended for cross platform support.
-code requestcodeThis tells
radpwtst to send (in addition to any other request
required) a RADIUS request with the given code name. Code names such as
Ascend-Access-Next-Code, Disconnect- Request and Change-Filter-Request
are all supported. Note that -code Status- Server
is identical in meaning to -status.
-acctonThis sends Accounting-On
request.
-acctoffThis sends Accounting-Off
request.
-identifier nThis is the identifier number
of a single RADIUS packet.
-no_randomThis forces
radpwtst to use fixed values for RADIUS
authenticator with different CHAP methods. This allows repeating tests
with known values.
-framed_ip_address addressAccess requests
are sent with the given Framed-IP-Address. The default value is
0.0.0.0. If the address is 0.0.0.0, it
is sent in the request. By default, radpwtst takes
notice of any Framed-IP-Address returned in an Access-Accept, and uses
it in subsequent Accounting Stops and Starts. Setting
-framed_ip_address causes the same address to be
used for all Accounting Stops and Starts.
-state stateThis adds the string as State
attribute.
-useoldascendpasswordsThis makes
radpwtst to encode passwords using the old (non-RFC
compliant) method that Ascend used to use for some NASs. The default is
to use RFC2865-compliant algorithm.
-incrementuserThis increments the user name
on each round. If the user name on the first round is
mikem001, it changes automatically to
mikem002 on the second round.
-nas_ip_address addressAccess and Accounting
requests have NAS-IP-Address of address. The default value is
203.63.154.1.
-nas_identifier identifierAccess and
Accounting requests have NAS-Identifier of identifier. The default value
is 203.63.154.1.
-nas_port portAccess and Accounting request
have NAS-Port of port. The default value is
1234.
-nas_port_type typeAccess and Accounting
request have NAS-Port-Type of type. The default
value is Async.
-service_type serviceAccess and Accounting
request have Service-Type of service. The default
value is Framed-User.
-called_station_id stringAccess and
Accounting requests have Called-Station-Id of
string. The default value is
123456789. If set to an empty string, Called-Station-Id
is not included in the request.
-calling_station_id stringAccess and
Accounting requests have Calling-Station-Id of
string. The default value is
987654321. If set to an empty string,
Calling-Station-Id is not included in the request.
-session_id stringAccounting request has
Acct-Session-ID of string. The default value is
00001234.
-session_time nAccounting request has
Acct-Session-Time of n. The default value is
1000.
-delay_time nAccounting request has
Acct-Delay-Time of n. The default value is
0.
-input_octets nAccounting request has
Acct-Input-Octets of n. The default value is
20000.
-output_octets nAccounting request has
Acct-Output-Octets of n. The default value is
30000.
-timeout nThis specifies the time in seconds
that radpwtst waits for a reply. The default value
is 5 seconds. If you specify 0, it
does not wait for a reply at all.
-noreplyWhen using this, no reply is waited
before sending another request.
-retries nIf there is no reply, send up to
n retries . The default value is 0
and no retries are sent.
-dictionary file,fileThis uses
file as the dictionary file. Multiple dictionary
files can be specified as comma-separated file names. If
-dictionary is not specified,
radpwtst loads automatically for the first file
that exists from this list ($radpwtstdir is the location where
radpwtst resides):
$radpwtstdir/dictionary/etc/radiator/dictionary/usr/local/etc/raddb/dictionary/usr/local/etc/radiator/dictionary/opt/radiator/radiator/dictionaryC:\Program Files\Radiator\dictionary
-class stringThis makes
radpwtst to send string as the Class attribute in
any accounting requests. Class defaults to the Class returned by any
previous access-accepts.
-message_authenticatorThis sends a correctly
calculated Message-Authenticator attribute with the
request.
Note
Some requests automatically add a
Message-Authenticator. For example, EAP requires
Message-Authenticator.
-no_message_authenticatorDo not
automatically add a Message-Authenticator attribute.
-raw dataThis sends raw data literally. An
example of suitable raw data is trace 5 packet dump output. White space
in the data is ignored.
-rawfile filenameThis reads raw data from
file called filename and send it literally. Raw
data can be split to multiple lines
-rawfileseq filenameRead a sequence of raw
data from file called filename and send it
literally. The requests are separated with delimiter
‘NewPacket’.
-outport portThis reads
radpwtst to send requests from the given port. Port
can be a port number or a port service name as used in
/etc/services or it equivalent on your system. The
default value is 0, meaning allocate a random
port.
-bind_address addressThis m
radpwtst to send requests through the network
interface for the given IP address. Requests appear to originate from
the specified IP address The default value is 0.0.0.0,
which means the default address of the default network interface. If the
destination address (such as the -s flag) is an
IPv6 address and -bind_address is specified,
bind_address must also be an IPv6 address.
-options optionfile
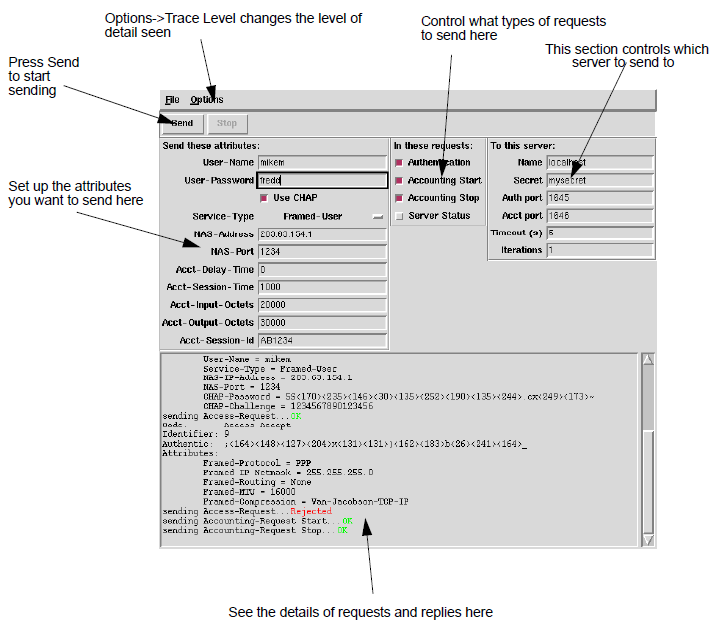
-guiThis presents A GUI that allows easy
interactive testing. This GUI runs on Unix, it is not yet available on
Windows hosts. Requests are sent when the Send button is pressed, and
the GUI stays up after the requests have been sent, so you can send
more. Requires Perl Tk module.
attribute=valueYou can force any number of
additional attributes to be sent in each request by naming them with
their values on the command line. attribute must be
the name of an attribute in your dictionary, and value must be a valid
value for that attribute.